Tag: equities
Investing Where the Puck Is Going: The Renewed Case for Active and Value (June 2025)
Insights from the Value Equities Investment Committee | PDF
“I skate to where the puck is going to be, not where it has been.” – Wayne Gretzky
With the Stanley Cup finals beginning last week in Edmonton — home to The Great One’s four championships — we’re reminded that Gretzky’s approach to hockey can offer valuable lessons for investors as well. Anticipating what is likely to occur and positioning oneself accordingly, rather than focusing on what has transpired, is as relevant on the ice as it is in today’s evolving investment landscape, one that has tended to favor passive investing and growth strategies.
Where Have We Been?
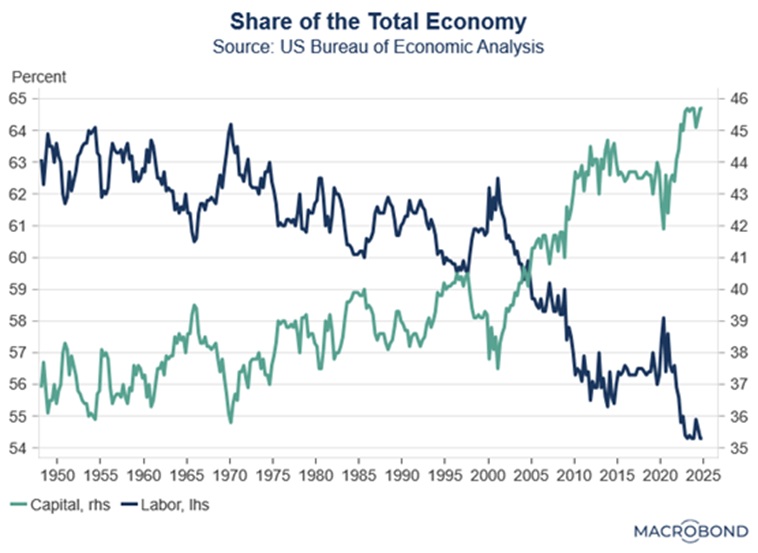
For decades, investors benefited from a backdrop of easing inflationary pressures and declining interest rates, a trend that began in the early 1980s and was fueled by technological advancements, deregulation, and expanding global trade. However, China’s entry into the World Trade Organization in 2001 accelerated the shift of manufacturing overseas, benefiting capital holders while suppressing wage growth for labor. Although consumers enjoyed lower prices, this dynamic contributed to rising income inequality and growing social frustration — a trend reflected in the rise of populist movements both in the US and abroad, exemplified by the campaigns of Bernie Sanders, Donald Trump, and Brexit. Today, we see renewed efforts to restructure trade and bring manufacturing back home, addressing the concerns of Main Street.
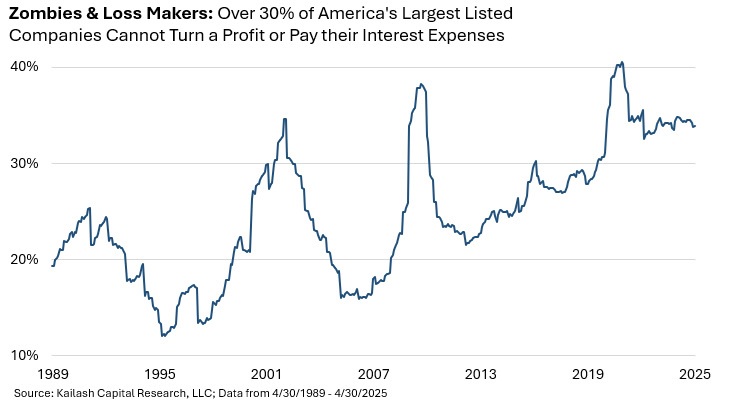
The era following the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) of 2008-09 was marked by unprecedented monetary stimulus. Central banks implemented Zero Interest Rate Policy (ZIRP) and Quantitative Easing (QE), flooding the system with liquidity. These measures kept real interest rates negative, which encouraged spending and investment by making cash holdings unattractive. While these policies shortened the recession, their prolonged use led to riskier capital allocation, with investors prioritizing growth over profitability. As a result, over 30% of public companies are now unprofitable compared to less than 20% before the GFC. Low inflation during this period also enabled governments to run large fiscal deficits, even during peacetime and economic expansion, pushing national debt to record levels relative to GDP.
Passive investing — allocating capital without regard to valuation and in proportion to company size — tends to be rewarded during the later stages of rising markets and periods of low volatility. The late stages can be especially rewarding as new flows are directed proportionally to larger businesses, which have more influence, creating a self-reinforcing cycle. The recent extended economic cycles, with two of the last three being the longest on record, were supported by subdued inflation and accommodative monetary policy. This environment, often described as the “Fed Put,” provided a safety net for investors and helped suppress market volatility.
Where Are We Going?
Today, the landscape is changing. Populism has gained traction, driving policies that aim to benefit Main Street. Tariffs on Chinese goods, initiated under President Trump during his first term and maintained by President Biden, seek to rebalance trade and revive domestic manufacturing. The current Trump administration is also continuing the prior administration’s challenge of monopolistic practices, particularly among large technology firms that have disproportionately benefited capital. These shifts are likely to keep upward pressure on inflation.
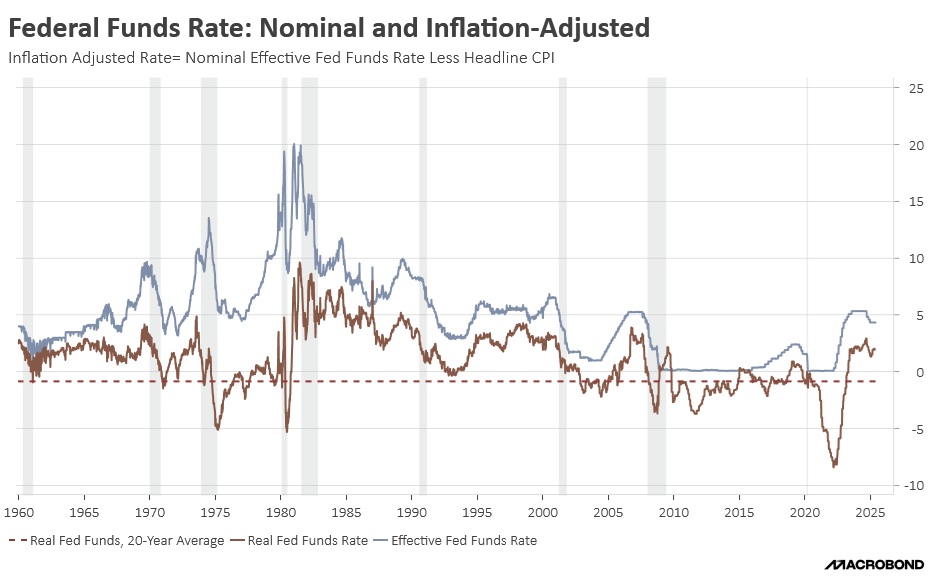
Rising inflation has already pushed interest rates higher, ending the era of negative real rates that distorted capital allocation. In this new environment, businesses must focus on generating higher returns on capital to offset increased borrowing costs, bringing fundamentals and valuations back into focus. Moreover, high inflation and elevated national debt will make it difficult to return to the ultra-loose monetary policies of the past.
As a result, investors should prepare for shorter economic cycles, higher interest rates, and increased market volatility. Historically, such conditions have favored active investing and value-oriented strategies over passive investing and growth-focused approaches.
As active managers, we at Confluence take a fundamental approach, one that focuses on understanding and valuing individual businesses with an emphasis on owning competitively advantaged companies trading at attractive valuations. Our active investment approach has been successfully implemented across numerous market cycles over the past three decades.
In light of the current market environment, we believe it’s time to skate to where the puck is going — not where it’s been.
Confluence of Ideas – #42 “Reviewing the Asset Allocation Rebalance: Q2 2025” (Posted 5/14/25)
Confluence of Ideas – #41 “Reviewing the Asset Allocation Rebalance: Q1 2025” (Posted 2/12/25)
Confluence of Ideas – #38 “Reviewing the Asset Allocation Rebalance: Q4 2024” (Posted 11/11/24)
Confluence of Ideas – #37 “Reviewing the Asset Allocation Rebalance: Q3 2024” (Posted 9/11/24)
Asset Allocation Bi-Weekly – #121 “Small Caps and the Hope for a Soft Landing” (Posted 6/24/24)
Asset Allocation Bi-Weekly – Small Caps and the Hope for a Soft Landing (June 24, 2024)
by the Asset Allocation Committee | PDF
They don’t call him Maestro for nothing. In the mid-1990s, Federal Reserve Chair Alan Greenspan achieved what was once thought of as impossible: an economic soft landing. As the US labor market showed signs of tightening, he raised interest rates from 3% to 6% in 1994 to preemptively combat inflation. In 1995, he lowered rates strategically to avoid a recession. The seamless transition from a tightening cycle to an easing cycle led some to believe the Fed could pull the strings in the economy in a way that could both prevent a recession and tame runaway inflation.
The market took notice. Greenspan’s policies helped quell investor anxieties about a repeat of the inflationary surges that plagued the 1970s and early 1980s. Emboldened by this newfound confidence, investors poured money into smaller, unproven companies with strong earnings growth potential. This sentiment was epitomized in 1995, when tech guru Marc Andreessen and his partner Jim Clark did the unthinkable by taking their company, Netscape, public before it had turned a profit, paving the way for what is now viewed as the dot-com bubble.
Today’s elevated interest rate environment has sparked nostalgia for another soft landing. Eager for a repeat of Greenspan’s success, investors were waiting for a decline in rates to re-enter the market. However, their hopes were dashed in June 2023. Not only did Fed policymakers raise rates following the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank, but they also signaled their intention for two additional hikes that year. This spooked markets as investors were concerned that the central bank may keep rates high for long enough to tank the economy.
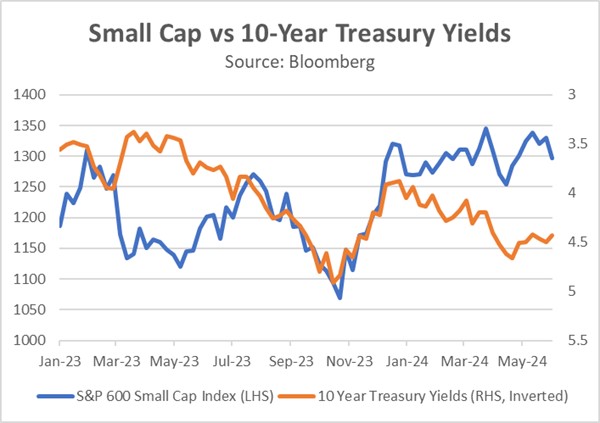
This commitment to raising interest rates discouraged investors from holding riskier assets, particularly those with floating rate exposure. Further pressuring the market were concerns about the rising national debt, which prompted Fitch to downgrade the US credit rating. Investors responded by offloading riskier assets within their portfolios. As a result, the 10-year Treasury yield soared to approximately 5%, a level not seen in over two decades, while the S&P SmallCap 600 Index plummeted to a nine-month low.
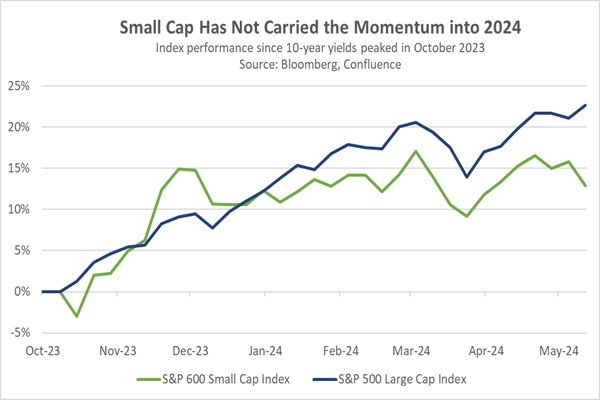
The tide began to turn in late October of last year. The US Treasury’s reallocation of bond issuance toward shorter maturities, coupled with Fed officials signaling an indefinite pause in rate hikes, significantly impacted market sentiment. Investors piled into longer-term bonds and risk assets in anticipation of the Fed’s next move, positioning themselves for an imminent rate cut, which they thought could take place in the first quarter of 2024. From October to December, the S&P SmallCap 600 Index outperformed the S&P 500, with a return of 21.5% compared to 13.7%, respectively.
Unfortunately, the early strength of small caps faded quickly as the S&P 500 recaptured its leadership position at the beginning of 2024. This new weakness in small caps stemmed from concerns that the Fed wouldn’t cut interest rates as deeply as the market anticipated, following a series of strong Consumer Price Index reports in the first quarter and a persistently tight labor market. This situation led investors to reduce their holdings of longer-term Treasurys and refocus on large cap companies due to their relatively strong earnings potential and resilience to changes in financial conditions.
In fact, recognizing this trend early on prompted us to take action in the second quarter. We strategically reduced our exposure to small cap stocks within the conservative portfolios of our Asset Allocation program. This decision also reflected our growing concern that small cap stocks may face longer-term challenges due to certain structural market factors, including the rising popularity of passive funds that funnel money into large cap stocks and the increasing ability of private equity firms to acquire the most promising small cap startups. Hence, an emphasis on quality while screening for indicators such as profitability, leverage, and cash flow should mitigate some of these factors.
Currently, the S&P SmallCap 600 Index has been in a holding pattern as investors await signals regarding the Fed’s next policy move. Should Chair Powell manage to orchestrate another soft landing in the coming months, it could attract investors back to small cap stocks. With the current multiples for the S&P 500 outpacing those of the S&P SmallCap 600 by the widest margin since the dot-com era, small cap stocks present appealing valuations compared to their larger counterparts. With that in mind, we think small cap stock values could rebound in the coming months if US economic growth remains healthy and both inflation and interest rates fall.