by Thomas Wash | PDF
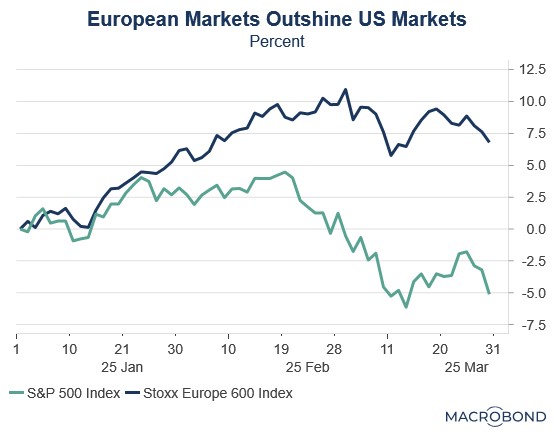
European equities have long suffered from investor skepticism and been burdened by perceptions of excessive regulation, bureaucratic inertia, and elevated operating costs. These structural challenges have historically overshadowed the region’s fundamental strengths. Yet 2025 has marked a striking reversal, with European stocks delivering exceptional returns that have handily surpassed US market performance.
Much of Europe’s recent outperformance relative to the US can be traced to the unwinding of the “Trump trade,” which began in the weeks following Donald Trump’s victory in the November 2024 election. During this time, markets seemed to embrace the narrative that his policies — deep tax cuts, aggressive deregulation, and a pro-growth agenda — would cement US economic dominance. While tariffs were always a part of the equation, investors initially expected them to be used selectively rather than aggressively.
While US equities surged after the November election, European stocks languished as investors anticipated a widening growth divide. The eurozone has now gone seven consecutive quarters without achieving 2% annualized growth in its gross domestic product, a streak dating back to the third quarter of 2022. Nowhere were these struggles more apparent than in Germany, where the industrial sector — traditionally the Continent’s economic powerhouse — became its biggest drag.
Market expectations shifted abruptly in the Trump administration’s early weeks as it simultaneously challenged existing trade arrangements and demanded greater military spending from allies. The tariff threats created immediate uncertainty as businesses shelved investment plans and consumers braced for inflationary pressures. Meanwhile, growing doubts about US security commitments prompted EU leaders to accelerate plans for strategic autonomy.
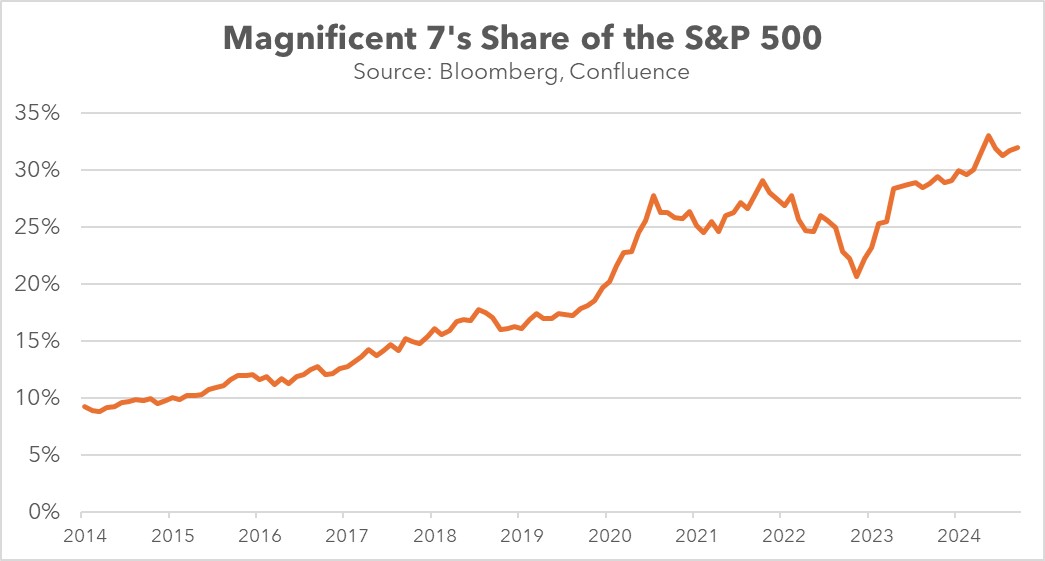
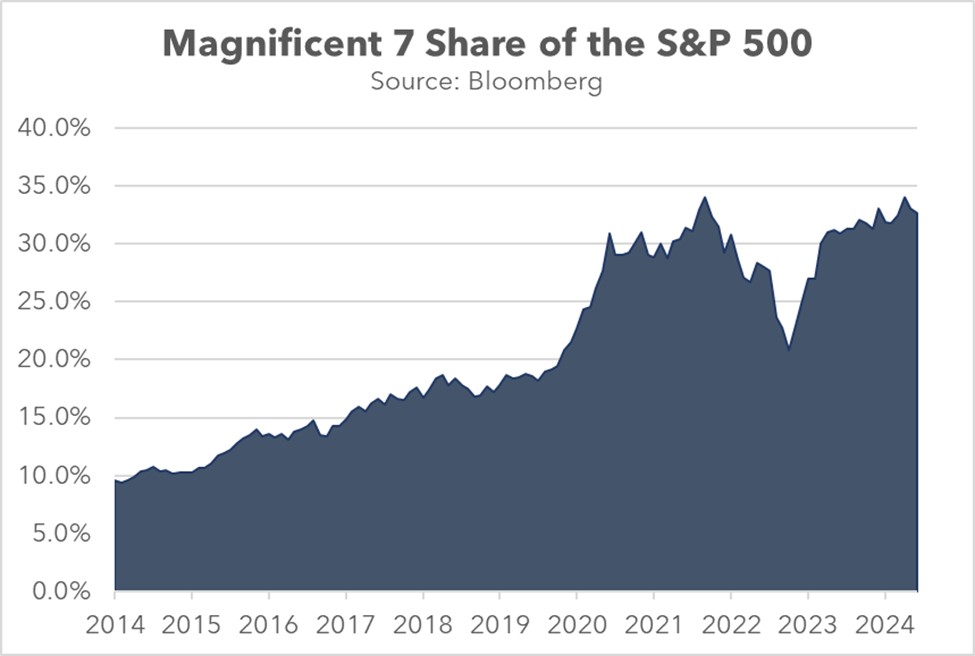
We think the rotation from US to European equities was primarily valuation-driven, with the US’s once-dominant Magnificent 7 declining as investors shifted from growth to value. This marked a dramatic reversal from previous years when tech-heavy growth stocks consistently outperformed. European markets, with their heavier weighting in value sectors and more attractive price-to-earnings ratios, became natural beneficiaries of this change in investor preference.
While capital rotation remains modest to date, escalating trade tensions may accelerate foreign divestment from US assets in favor of European markets. These geopolitical strains have triggered a broad risk-off shift among investors, with capital flowing toward value assets rather than growth equities. This reallocation reflects a fundamental reassessment of global trade dynamics as nations increasingly recognize that traditional US trade relationships may be changing for good.
This shifting sentiment marks a potential inflection point after years of sustained US equity outperformance. For decades, global investors have disproportionately favored US markets, having been lured by three key advantages: (1) superior growth prospects, particularly in the technology sector; (2) unrivaled market depth and liquidity; and (3) the structural strength of the dollar. These factors became particularly pronounced in the post-pandemic era when the greenback’s appreciation created an additional return tailwind for foreign investors.
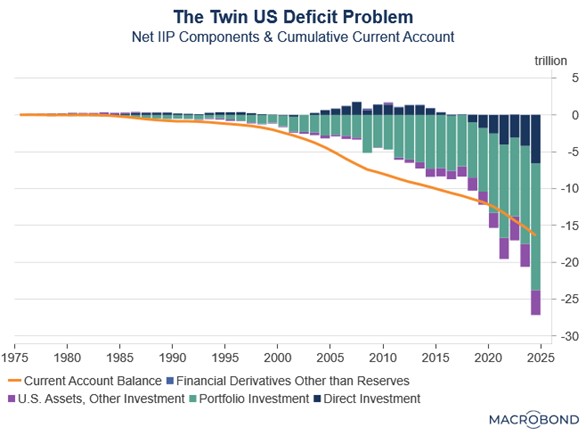
In an especially important development during this period, the US began running deficits in both its trade balance and its “primary income” balance. This twin deficit was problematic because it signaled that foreign investors were earning higher returns on their US investments than what US residents were earning abroad. In other words, the US was not only importing more than it exported but also paying out more in interest and dividends to the rest of the world than it was receiving.
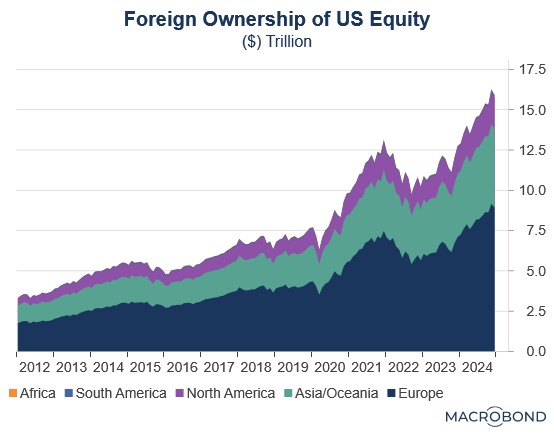
The growing imbalance stemmed from two key factors: persistent US equity outperformance relative to global markets and the Fed’s rate hikes that made Treasurys more attractive to foreign investors. These forces converged in the Net International Investment Position, resulting in the value of foreign-held US assets eclipsing America’s cumulative trade deficit for the first time ever. The shift reflected both a reversal from direct investment surplus to deficit and rising portfolio investment values — twin manifestations of superior US asset returns.
Typically, such conditions would prove problematic for most economies as they could trigger disproportionate currency outflows and subsequent depreciation or make its markets vulnerable to panics. However, the US dollar’s unique status as the global reserve currency and its deep and open capital markets have largely shielded it from these adverse effects.
Nevertheless, significant risks remain. US equity markets could experience heightened volatility should foreign investor sentiment deteriorate, with the technology sector being particularly vulnerable due to its elevated valuations. The scale of this exposure is evident in foreign holdings, which now compose over 30% of US equities, driven by a dramatic surge in both portfolio income and direct investment flows.
A sudden erosion of confidence in US equities could precipitate a significant capital rotation into foreign equities and gold. Europe appears particularly well-positioned to benefit from this shift, owing to its relative valuation discount and potential for capital repatriation flows. Within the region, Germany stands out as especially attractive given its increased defense spending commitments. Meanwhile, gold could emerge as the safe-haven asset of choice, with the potential to displace US Treasurys as a reserve asset over time.